B-hSIRPA mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Sirpatm1(SIRPA)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hSIRPA mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 110016 |
|
Aliases |
Sirpa (signal-regulatory protein alpha) |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
19261 |
||
mRNA expression analysis
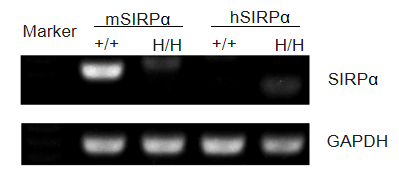
Strain specific analysis of Sirpα gene expression in WT and B-hSIRPA mice by RT-PCR. Mouse Sirpα mRNA was detectable in splenocytes of wild-type (+/+) mice. Human SIRPα mRNA was detectable only in H/H but not in +/+ mice.
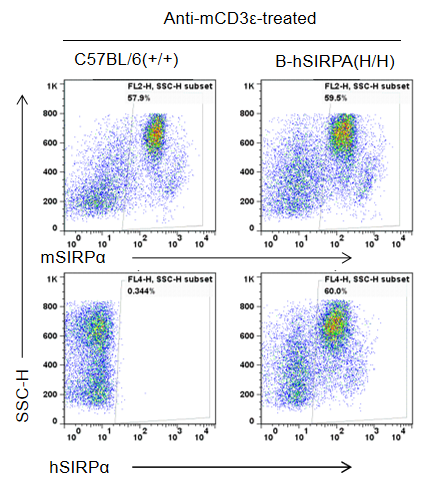
Species specific SIRPα expression analysis in B-hSIRPA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from WT and homozygous B-hSIRPA (H/H) mice stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti- SIRPα antibodies. Mouse SIRPα was detectable in WT mice. This anti-mouse SIRPα antibody also cross reacts with human SIRPα. Human SIRPα were exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hSIRPA mice but not in WT mice.
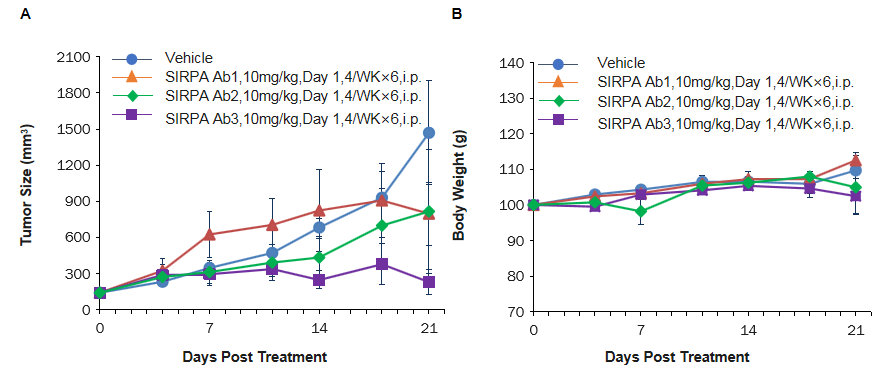
Antitumor activity of anti-human SIRPα antibodies in B-hSIRPA mice. (A) Anti human SIRPα antibodies inhibited MC38-hCD47 tumor growth in B-hSIRPA mice. Murine colon cancer MC38-hCD47 cells (5×105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hSIRPA mice (male, 9-week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150mm3, at which time they were treated with three anti-human SIRPα antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human SIRPα antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hSIRPA mice, demonstrating that the B-hSIRPA mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human SIRPα antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
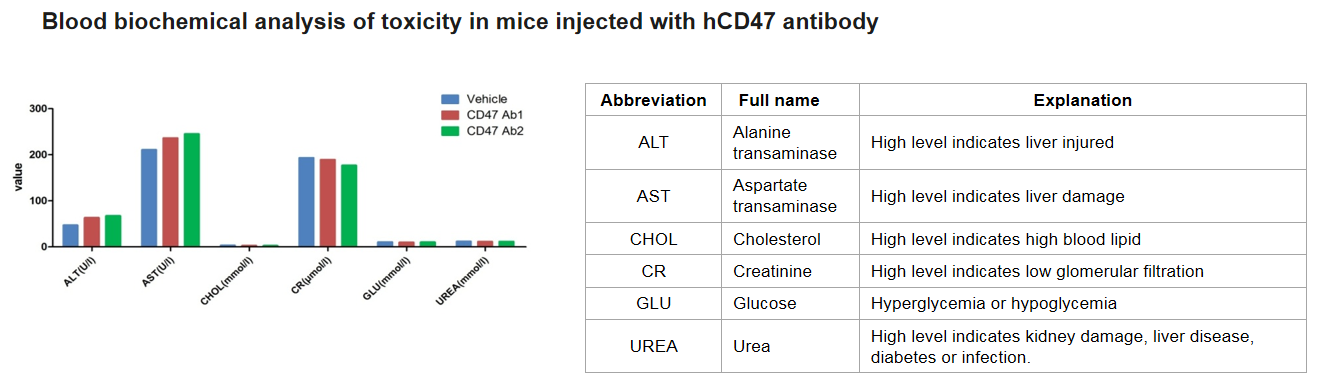
Homozygous B-hCD47 mice were I.P. injected with anti-hCD47 antibodies. Blood from each mice were collected and Blood Biochemical Test was conducted. Blood from Ab3 and Ab5 groups were not analyzed because of death of the treated mice.
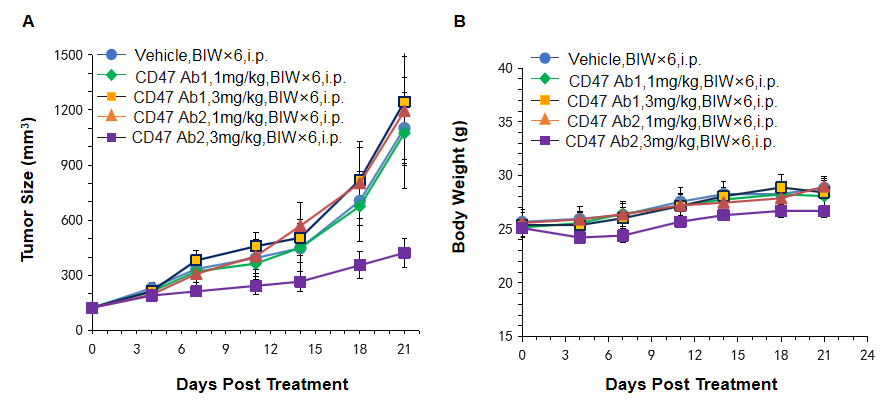
Antitumor activity of anti-human CD47 antibody in B-hCD47 mice and C57BL/6 mice. Anti-human CD47 antibody inhibited MC38-hCD47 tumor growth in B-hCD47 mice. (A) Murine colon cancer MC38-hCD47 cells (5×105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hCD47 mice (female, 6 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150 mm3, at which time they were treated with two anti-human CD47 antibodies and schedules indicated in panel A, as shown in panel A, 3 mg/kg of anti-human CD47 Ab2 was efficacious in controlling tumor growth in the homozygous B-hCD47 mice.(B)Body weight. The results demonstrating that B-hCD47 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.











